reworking content
All checks were successful
learn org at code.softwareshinobi.com/linux.softwareshinobi.com/pipeline/head This commit looks good
All checks were successful
learn org at code.softwareshinobi.com/linux.softwareshinobi.com/pipeline/head This commit looks good
This commit is contained in:
50
landing/docs/Commands/disk/fdisk.md
Normal file
50
landing/docs/Commands/disk/fdisk.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,50 @@
|
||||
# The `fdisk` command
|
||||
|
||||
The `fdisk` command is used for controlling the disk partition table and making changes to it and this is a list of some of options provided by it : </b>
|
||||
- Organize space for new drives.
|
||||
- Modify old drives.
|
||||
- Create space for new partitions.
|
||||
- Move data to new partitions.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Examples:
|
||||
|
||||
1. To view basic details about all available partitions on the system:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
fdisk -l
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. To show the size of the partition:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
fdisk -s /dev/sda
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
3. To view the help message and all options of the command:
|
||||
```
|
||||
fdisk -h
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Syntax:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
fdisk [options] device
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Some of the command options:
|
||||
|
||||
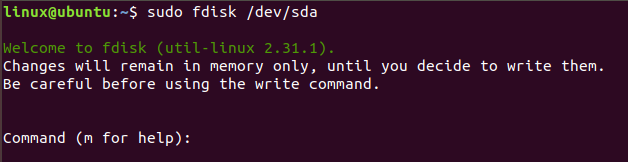
On writing the following command
|
||||
```
|
||||
fdisk /dev/sdb
|
||||
```
|
||||
the following window appears :
|
||||
|
||||
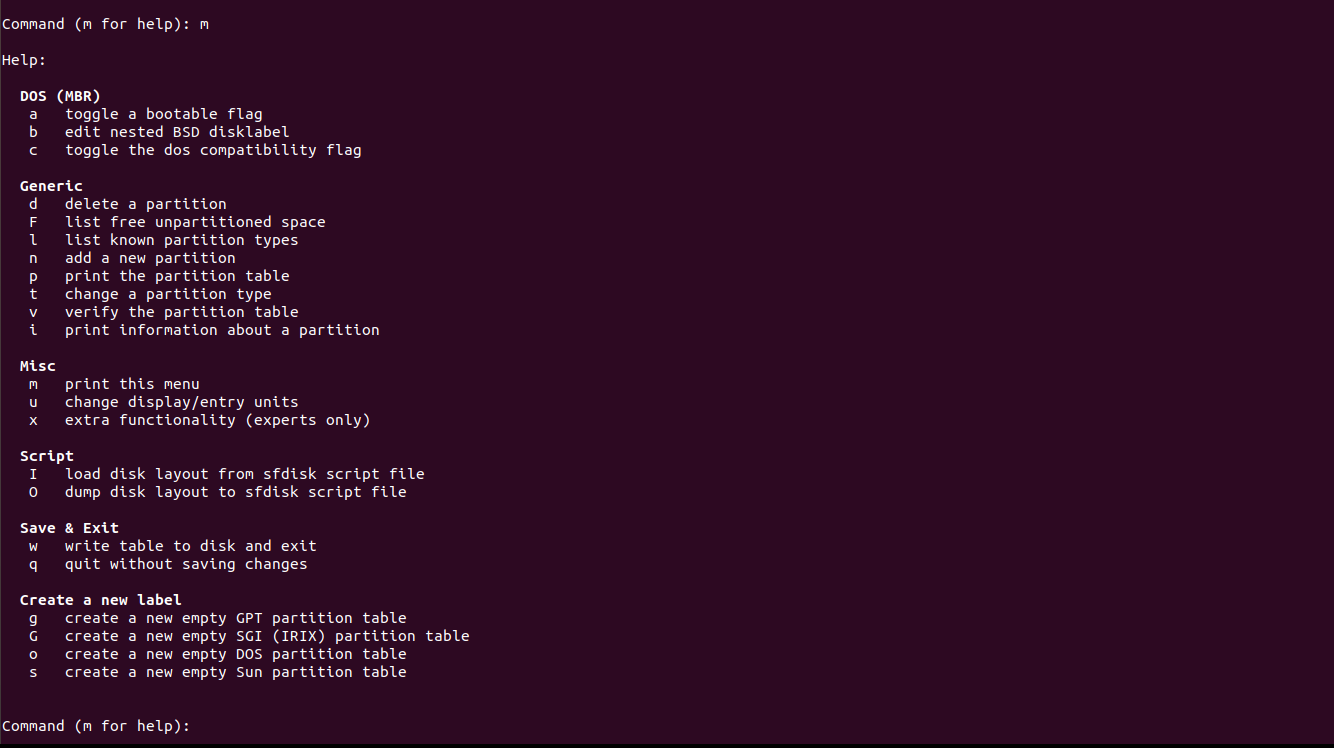
and then you type m which will show you all options you need such as creating new partition and deleting a partition as in the following picture :
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
44
landing/docs/Commands/disk/mount.md
Normal file
44
landing/docs/Commands/disk/mount.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
|
||||
# The `mount` command
|
||||
|
||||
The `mount` command is used to mount 'attach' a filesystem and make it accessible by an existing directory structure tree.
|
||||
### Examples:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Displays version information:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mount -V
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Attaching filesystem found on device and of type type at the directory dir:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mount -t type device dir
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Syntax Forms:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
mount [-lhV]
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
mount -a [-fFnrsvw] [-t vfstype] [-O optlist]
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
mount [-fnrsvw] [-t fstype] [-o options] device dir
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Additional Flags and their Functionalities:
|
||||
|
||||
|**Short Flag** |**Long Flag** |**Description** |
|
||||
|:---|:---|:---|
|
||||
|`-h`|<center>`--help`</center>|Dispaly a help message and exists|
|
||||
|`-n`|<center>`--no-mtab`</center>|Mount without writing in /etc/mtab|
|
||||
|`-a`|<center>`--all`</center>|Mount all filesystems (of the given types) mentioned in fstab|
|
||||
|`-r`|`--read-only`|Mount the filesystem read-only|
|
||||
|`-w`|`--rw`|Mount the filesystem as read/write.|
|
||||
|`-M`|`--move`|Move a subtree to some other place.|
|
||||
|`-B`|`--bind`|Remount a subtree somewhere else *(so that its contents are available in both places)*.|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
75
landing/docs/Commands/disk/parted.md
Normal file
75
landing/docs/Commands/disk/parted.md
Normal file
@@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
# The `parted` command
|
||||
|
||||
The `parted` command is used to manage hard disk partitions on Linux. It can be used to add, delete, shrink and extend disk partitions along with the file systems located on them.
|
||||
You will need root access to the system to run `parted` commands.
|
||||
|
||||
**NOTE:** Parted writes the changes immediately to your disk, be careful when you are modifying the disk partitions.
|
||||
### Examples:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Displays partition layout of all block devices:
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo parted -l
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Display partition table of a specific `disk`
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo parted disk print
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Examples of `disk` are /dev/sda, /dev/sdb
|
||||
|
||||
3. Create a new disk label of `label-type` for a specific disk
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo parted mklabel disk label-type
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`label-type` can take values "aix", "amiga", "bsd", "dvh", "gpt", "loop", "mac", "msdos", "pc98", or "sun" <br />
|
||||
|
||||
4. Create a new partition in a specific `disk` of type `part-time`, file system is `fs-type` and of size `size` Mb.
|
||||
```
|
||||
sudo parted disk mkpart part-time fs-type 1 size
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`part-time` can take values "primary", "logical", "extended".<br />
|
||||
`fs-type` is optional. It can take values "btrfs", "ext2", "ext3", "ext4", "fat16", "fat32", "hfs", "hfs+", "linux-swap", "ntfs", "reiserfs", "udf", or "xfs"<br />
|
||||
`size` has to less than the total size of the specified disk. To create a partition of size 50Mb, <size> will take the value of 50
|
||||
|
||||
5. `parted` can also be run in an interactive format. Operations to manage the disk partitions can be performed by entering appropriate commands in the interactive session.
|
||||
`help` command in the interactive session shows a list of all possible disk management operations which can be performed.
|
||||
```
|
||||
$ sudo parted
|
||||
GNU Parted 3.3
|
||||
Using /dev/sda
|
||||
Welcome to GNU Parted! Type 'help' to view a list of commands.
|
||||
(parted) print # prints the partition table of the default selected disk - /dev/sda
|
||||
Model: ATA VBOX HARDDISK (scsi)
|
||||
Disk /dev/sda: 53.7GB
|
||||
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/512B
|
||||
Partition Table: msdos
|
||||
Disk Flags:
|
||||
|
||||
Number Start End Size Type File system Flags
|
||||
1 1049kB 53.7GB 53.7GB primary ext4 boot
|
||||
|
||||
(parted) select /dev/sdb # change the current disk on which operations have to be performed
|
||||
Using /dev/sdb
|
||||
(parted) quit # exit the interactive session
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Syntax Forms:
|
||||
```
|
||||
parted [options] [device [command [options...]...]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Options:
|
||||
|**Short Flag** |**Long Flag** |**Description** |
|
||||
|:---|:---|:---|
|
||||
|-h|--help|displays a help message listing all possible `commands [options]`|
|
||||
|-l|--list|lists partition layout on all block devices|
|
||||
|-m|--machine|displays machine parseable output|
|
||||
|-v|--version|displays the version|
|
||||
|-a|--align|set alignment type for newly created partition. It can take the following values:<br /> `none`: Use the minimum alignment allowed by the disk type<br /> `cylinder`: Align partitions to cylinders<br /> `minimal`: Use minimum alignment as given by the disk topology information<br /> `optimal`: Use optimum alignment as given by the disk topology information|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user